What is a HoneyPot?
Description of honeypot
One definition of honeypot comes from the world of espionage, where Mata Hari style spies who use romantic relationships as a way to steal secrets are described as setting a ‘bee trap’ or ‘honeypot’. Usually, the enemy spy is threatened with a beehive and forced to pass on all he knows.
In terms of computer security, cyber honeypot works in a similar way, setting a trap for hackers. It is a self-sacrificing computer program that aims to attract cyber attacks, such as deception. It mimics targeted hackers, and uses their login attempts to obtain information about criminal activity in practice or to interfere with other purposes.
How HoneyPot Works
Honeypot looks like a real computer program, with applications and data, tricking cybercriminals into thinking that it is a legitimate target. For example, a honeypot could mimic a corporate customer billing system - mainly targeted at criminals who want to get credit card numbers. As soon as hackers enter, they can be tracked, and their behavior is tested on how to make the real network safer.
Honeypots are designed to attract attackers by building on deliberate security risks. For example, a honeypot may have ports that respond to port scans or weak passwords. Dangerous ports can be left open to attract invaders into the honeypot area, rather than a much safer live network.
Honeypot is not set to deal with a specific problem, such as a firewall or an anti-virus. Instead, it is an information tool that can help you understand the threats that exist in your business and detect the emergence of new threats. With the wisdom found in the honeypot, security efforts can be prioritized and focused.
Different types of honeypot and how they work
Different types of honeypot can be used to identify different types of threat. Different definitions of honeypot are based on the type of threat it is targeting. They all have a place in the realm of complete and effective cyber security strategies.
Email traps or spam traps place a false email address in a hidden area where only the default address harvester will be able to find it. Since the address can be used for any purpose other than the spam trap, it is 100% certain that any email you receive is spam. All messages containing the same content as those sent to the spam trap can be automatically blocked, and the sender's IP source can be added to the denial list.
A decoy database can be set up to monitor software vulnerabilities and virtual attacks using unsafe system configuration or using SQL injection, exploitation of SQL services, or copyright infringement.
The Malware honeypot mimics software applications and APIs inviting malware attacks. Malware features can be analyzed to improve anti-malware software or to prevent vulnerability in the API.
Spider honeypot is designed to capture webcrawlers ('spiders') by creating web pages and links that are accessible only to webpages. Finding pages can help you learn to block bad bots, as well as web ad pages.
By monitoring traffic entering the honeypot system, you can check:
- where cyber criminals appear
- threat level
- they use any modandi operandi
- what data or applications they are interested in
- how effective are your security measures in preventing cyber attacks
Another definition of honeypot looks at whether the honeypot is high-performance or low-level. Slightly interactive honeypots use fewer resources and collect basic information about the level and type of threat and where it comes from. Simple and quick to set up, they usually have some basic TCP and IP processes as well as network services. But there is nothing in the honeypot to engage the attacker for a long time, and you will not find detailed information about their practices or complex threats.
In the field of cyber security there is always the question of how to catch a criminal if we try to hack our system? So the basic answer is that we can set a trap for hackers this type of trap called honeypot.
Even many large companies use smart honeypots, such as Google, Facebook, Microsoft to monitor their users and activities if they find any illegal or dangerous activity the honeypot can block IP.
Honeypots are divided into two types of distribution base and construction base
Posting basis
- Honeypot production
- Honeypot survey
The Basis of the Design
- Clean Honeypot
- High Honeypot interaction
- Low Honeypot interaction
Play Install And Use Video
Play Live Video :- ▶ Play Video
Install and Set Up Honeypot in Linux
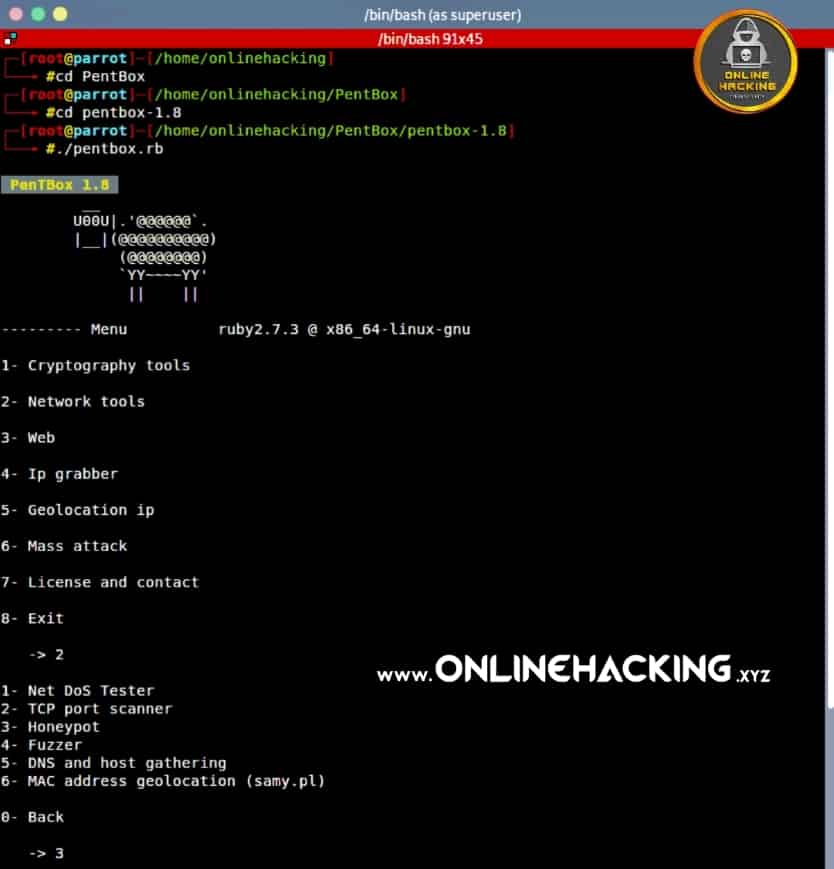
To set the honeypot in our Kali Linux system we need to download a tool from github called Pentbox. This tool is written in ruby language. To download this we use the following command:
A screenshot of this command follows:
After that we need to enter the pentbox folder using the cd command as follows:
Here we have a compressed file called pentbox.tar.xz and to extract it using the following command:
Now go to pentbox-1.8 and look for files using the following command:
We then use this ruby tool using a simple command as follows:
After that the tool will open
Here we need to go to the network tools option so type 2 and press Enter.
Yes, we now see the Honeypot option so we select it by selecting option 3.
Screenshot follows:
Now you can see that there are two options, with which you can set up your honeypot.
a) Instant Automatic Repair
b) Manual Modification (for Advanced Users)
You can choose any option but it is also easy for newbies users, you can choose the default default setting. As you can see, the honeypot starts at the top screen.
As you can see, your honeypot will only monitor all activities in PORT 80, but if you want to monitor other activities in another port, you can select the second Document Correction option.
Port 80 means that, when someone opens your IP / Host in their web browser, they will immediately record that request and display all possible information for this application as shown below:
Details you can see:
- IP address
- Details of his OS
- Web browser
- etc.
Under the same Network tools, there are also some exciting options such as "Net Dos Tester" that you can easily use DOS for someone who is affected by SYN and TCP floods.
The Dangers of HoneyPots
While the safety of the honeypot will help to plan a threatened environment, honeypots will not see everything that happens - only the work directed at the honeypot. Just because a certain threat is not directed at the honeypot, you cannot assume that it does not exist; it is important to keep up with IT security issues, not just rely on honeypots to inform you of threats.
A beautiful, well-prepared honeypot will mislead attackers into believing they have access to the real system. There will be the same login warning messages, the same data fields, and the same look and feel of logos as your actual applications. However, if the attacker was able to identify you as a honeypot, he could continue to attack other of your systems while leaving the honeypot untouched.
Once the honeypot has been fitted with a 'fingerprint', the attacker can create a vicious attack to distract attention from the actual exploitation targeted by your production plans. They can also feed bad information on the honeypot.
What’s worse is that a smart attacker can use the honeypot as a way to your systems. That’s why honeypots will never replace adequate security controls, such as firewalls and other access access systems. Since the honeypot can serve as an indoor introductory pad, make sure all honeypots are well secured. ‘Honeywall’ can provide basic honeypot security and stop honeypot-targeted attacks from entering your live system.
Honeypot should provide you with information to help prioritize your cyber security efforts - but it cannot restore the proper cyber security. Even if you have a lot of honeypots, consider a package like Kaspersky's Endpoint Security Cloud to protect your business assets. (Kaspersky uses its honeypots to detect online threats, so it is not necessary.)
All in all, the benefits of using honeypots far outweigh the risks. Hackers are often thought of as a distant, invisible threat - but using honeypots, you can see exactly what they are doing, in real time, and then use that information to stop them from getting what they want.





SOCIAL MEDIA